|
|
 发表于 2007-5-30 11:32:44
|
显示全部楼层
发表于 2007-5-30 11:32:44
|
显示全部楼层
In the setting value simulation module, the fault can be
classified into line fault and bus fault. The line fault locality
should be given. There are four system fault types, namely,
three-phase short-circuit fault, line-to-line, single line-to-earth
and two-phase line-to-earth. There are four protection class of
setting simulation: they are phase-to-phase over-current
protection, phase-to-phase distance protection, zero-sequence
over-current protection and ground distance protection.
In the setting value simulation process, when T=Os, the
setting value simulation is started. At first, set the fault locality
and select the fault equipment, type and the simulated
protection class. Then set the reject-action breaker and the
power system operation condition. Pressing the 'simulation'
button, the simulation system begins to work. The likely tripout
breakers will be searched with the intelligent searching
technology.
The intelligent searching method will search the likely tripout
protection device according to the fault type and
protection device configuration combined with the database.
A protection device framework array TMB is set to record all
kinds of information and parameters for the protection device
performance. For the line fault, it will find the breakers
locality at the two terminals of the transmission line in the
database with the transmission line number and add them into
TMB array. If the transmission line breaker refuses to act, it
will find the back-up protection according to power network
topology parameters in the database and add them into TMB
array. For the bus fault, it will find all the breakers which
located on another terminal of the transmission line that
connects with this bus and add their information into TMB
array. When the breaker refuses to trip out, it will find the
back-up protection of the breaker with the network topology
parameters in the database and add them into TMB array.
All breaker information can be saved in TMB array by the
intelligent searching. The bus node number and the branch
line number of the breakers' position are used as node
parameter and line parameter to be measured and output. Put
them in the fault calculation module, start the fault calculation,
get the power network parameters from database, then do the
calculation according to fault setting parameters, and output
the measured voltages and currents of locations where those
breakers are set. After that, find out corresponding setting
value checking formula according to the simulated protection
type, calculate protection devices' measured value, and then
compare it with the value get from the database. If the action
condition is satisfied, the protection trips out. If it clears the
system fault correctly, then put out the simulation report, the
simulation is finished. If it cannot clear the fault completely,
then enter next simulation period of T=0.5s (the time of
second zone). Start logical judgment simulation now, search
breakers likely to act according to power network topology
information, and add them to TMB array. In addition, breakers
which have tripped out are not included. Compare the
measured value with the setting value and time delay in the
database, if criterion is tenable, the system fault will be
cleared. If the fault is not cleared completely, then turn to next
simulation period, do the logical judgment simulation until
simulation time is running out or the fault is cleared.
Otherwise, put out the simulation report, finish the simulation.
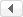
The power flow of simulation system is shown in figure 2. 71
Fault Locality Settirig Intelligent
l ~~~Searching fo- ewr
Network]|+Started Tplg
Topolog.y t perflow o t Protection
T Fault Cilculation Setting simu
1) fault escriptio, includig uthetie,posTin, Vandtye
Ou-t-put Electrc|I
o Measuringation cd Protection Relayin.
2) measurd d hLogi c Judgento
po Deviceake Protection Relaying
3Setting Valu e cekJuugdigecment t Protectior
4) protectio trip uiTrp ip Out
eProtectiio
|Tr ip Out Yes mu
; me En~~~im
I = ~~No F -TT+O0.5 <
Output Simulating t riaYes
Report
Fig.2 The power flow of the simulation system
The setting value simulation report summarizes simulation
data. Its contents are as follows:
1) fault description, including the time, position, and type
of the fault, the system operation condition.
2) measured data, the node voltage and line current of each
protection breaker in TMB array.
3) the setting value checkout, output the required formulas,
calculate setting value and time lag, then compare with the
given value.
4) protection trip out criterion, output the protection
breakers, the protection type and the time delay of the relay
protection.
5) simulation report, analyzing the rationality of the
protection setting value, output the simulation reports, at the
same time, feedback alarm signal on the breakers that tripped
out is given with multiform, such as graphs and sounds.
VI. GENERAL PERFOPMANCE
The computer visual technology and database technology
are employed to realize the friendly human being interface and
the function of powerful graph editing. It is convenient to set
or amend the power network parameters. All kinds of
parameters are analyzed and managed by the data
management module. Both the graph and data may be printed
out. The fault calculation and setting value simulation
checkout can be done well. Using the window integration
technology, it is very simple and advantageous for the system
operation. In addition, the software scalability and reusability
are improved by using the advanced COM technology to
encapsulate the program module.
The simulation system is developed as a continuation of the
visual relay protection setting calculation and management
system. It provides with a solution that the selectivity and
sensitivity of the setting value which calculated by setting
calculation and management system cannot be tested by real
4 |
|
 /1
/1